ChatGPT is still the world’s most popular large language model after pioneering the space two years ago, but other players are slowly catching up.
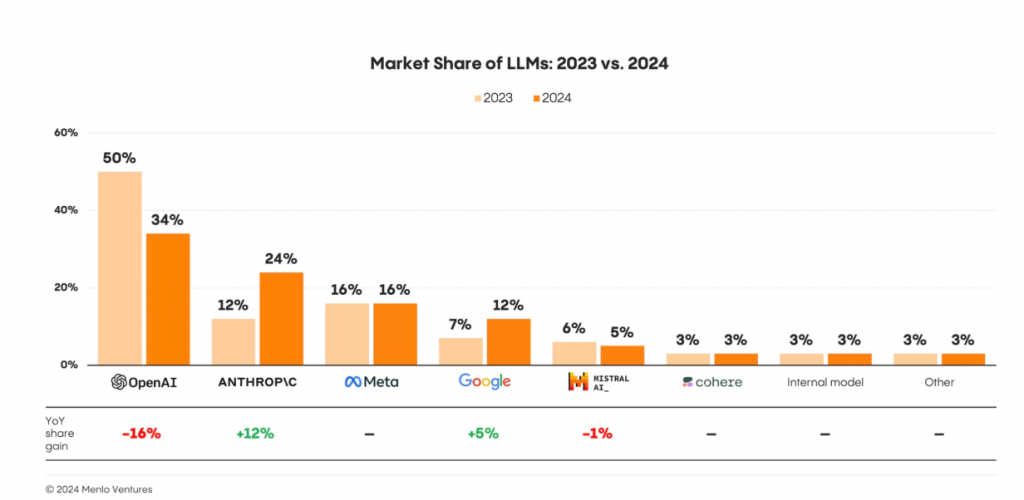
ChatGPT’s market share has fallen from 50 percent in 2023 to 34 percent in 2024, a report from Menlo Ventures has found. In comparison, Google’s Gemini saw its market share rise from 7 percent in 2023 to 12 percent in 2024. The biggest gain was seen with Anthropic’s Claude, which has seen its market share rise from 12 percent to 24 percent. Meta’s Llama series of models, which are available in several Meta products, saw their market share remain constant at 16 percent between 2023 and 2024.
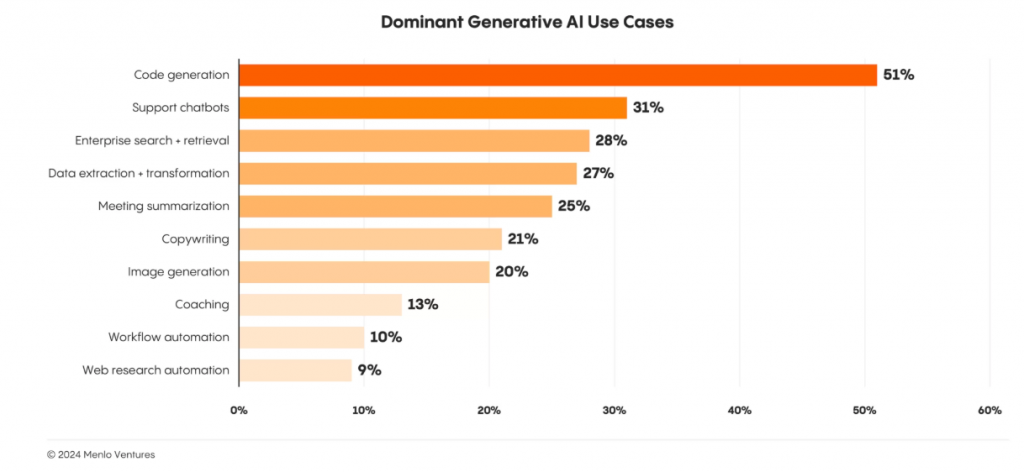
2024 was a breakout year for AI. AI spending in 2024 rose 6x, touching 13.8 billion USD compared to 2.3 billion USD spent in 2023. The biggest use of AI was in writing code, with 51 percent of respondents saying they were using it for coding, while 31 percent were using it for chatbots. An additional 21 percent were using it for copywriting.
But contrary to what many had predicted in the early days of the AI revolution, a handful of companies seem to be controlling most kinds of AI usage. It had at one point been believed that while LLM creators like OpenAI and Google would create solid foundational LLMs, they would require to be finetuned for specific use-cases. But as it turns out, foundational models have become uniformly strong over a wide variety of uses, making it unnecessary to fine-tune them. This has led to widespread adoption of AI, either directly through foundation models like GPT 4-o, Google’s Gemini or Anthropic’s Claude, or through companies which provide access to these models through suitable user interfaces.
To OpenAI’s credit, they’ve managed to still retain leadership in the space, even with the entry of players like Google, Meta, and companies founded by former OpenAI employees like Anthropic. But as the latest data shows, their lead is thinning, and other companies are eating into their market share. And this might be a good sign for the entire space — for one company to have complete domination over a technology as powerful as modern LLMs could’ve led to scope for misuse and price gouging, but with now a handful of LLMs of roughly equal capabilities available to users, it might lead to even more innovation in the AI space.